Frontotemporal dementia is a type of dementia characterized by progressive degeneration of the frontal and temporal lobes. FTDs typically manifest as gradual behavioral or language disorders. The three major subtypes or variant syndromes are behavioral variant (bvFTD), formerly known as Pick’s disease, and two variants of primary progressive aphasia – semantic variant (svPPA) and nonfluent variant (nvPPA) (nfvPPA).
Advertisement
Advertisement
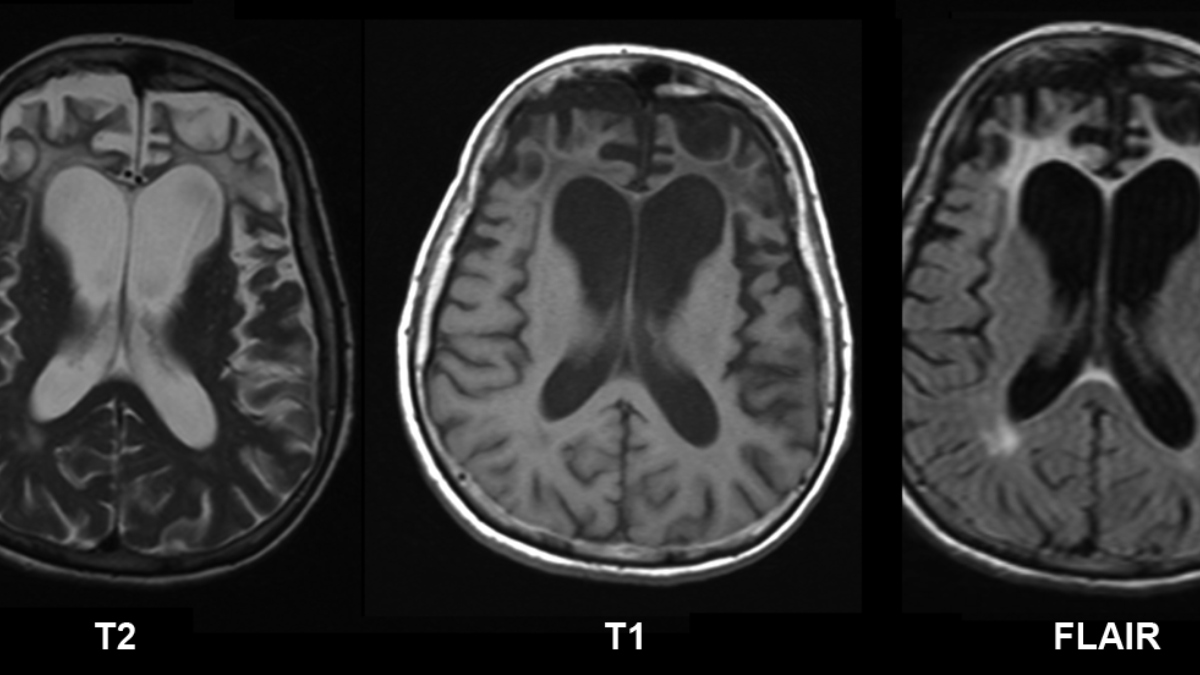
The International Classification of Diseases recognizes the disease as a cause of disorder affecting the mental and behavioral aspects of the human organism. Dissociation from family, extreme oniomania, vulgar speech characteristics, screaming, inability to control emotions, behavior, personality, and temperament are all characteristics of social display patterns. It has been reported that the gradual onset and progression of changes in behavior or language deficits began several years before presentation to a neurologist.
What are 5 extreme behavior changes found with FTD?
- Loss of empathy and other interpersonal skills, such as having sensitivity to another’s feelings.
- Lack of judgment.
- Loss of inhibition.
- Lack of interest (apathy), which can be mistaken for depression.
- Lack of social tact.

Leave a Reply